
Restriction enzymes (endonucleases). Cleave a specific DNA sequence Protect bacteria from phage infection by digesting phage DNA after infection. Cellular DNA is protected by methylases - block restriction enzyme activity. Each organism has a specific set of restriction enzymes:.

liv + Follow
Download PresentationAn Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Content is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use only. Download presentation by click this link. While downloading, if for some reason you are not able to download a presentation, the publisher may have deleted the file from their server. During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher.

Restriction Enzymes and DNA Fingerprinting. Molecular Scissors for Cutting DNA Precisely. Its because of these biological catalysts that genetic engineering is possible Restriction enzymes can also be called Endonucleases . Types of Restriction Enzymes. Type I
1.18k views • 11 slides
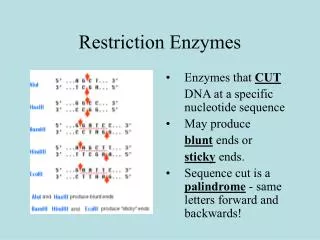
Restriction Enzymes. Enzymes that CUT DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence May produce blunt ends or sticky ends. Sequence cut is a palindrome - same letters forward and backwards! . Blunt End Cuts. Used to isolate a fragment of DNA
893 views • 7 slides

Discovered in bacteria Allow bacteria to protect themselves from viri Specialized proteins (enzymes) that act as nucleases Break bonds between nucleotides (building blocks of nucleic acids, including DNA) Recognize specific, short sequences of nucleotides in DNA
248 views • 6 slides

RESTRICTION ENZYMES & GENETIC RECOMBINATION. BIOLOGY 2/2A Motzko. Saccharin (1879). Corn Flakes (1899). Microwave Oven (1945). Penicillin (1927). Werner Arber (1969) 1 st To Isolate Restriction Endonucleases (Enzymes). Restriction Endonucleases.
444 views • 21 slides

Restriction Enzymes and Gel Electrophoresis. Genetics 335. Step 1: Restriction enzymes/endonucleases. Enzymes that cut DNA into fragments of different sizes Cleave DNA at specific phosphodiester bonds Named after bacterial strains E.g., BamHI, EcoRI, HAEIII, HindII, MstII
306 views • 8 slides

Restriction Enzymes. Aims: Must be able to recall the basic functions of restriction enzymes. Should be able to outline how specific restriction enzymes work. Could be able to explain the different ends produced by restriction enzymes and their benefits. Restriction Enzymes.
896 views • 7 slides
DNA. Restriction enzymes. Restriction Enzymes. Heparan ase = enzyme. Problem: Is heparanase important in bone development? Hypothesis: If heparanase is overexpressed, then bone formation will abnormal.
221 views • 6 slides

Practical Of Genetics. Restriction Enzymes. Lab.7. Objectives:. Introduce the students to digest genomic DNA by restriction endonucleases. Observe the results of digestion on agarose gel electrophoresis. Introduction:.
823 views • 29 slides

Restriction Enzymes. Restriction Endonucleases. Also called restriction enzymes 1962: “molecular scissors” discovered in in bacteria E. coli bacteria have an enzymatic immune system that recognizes and destroys foreign DNA
737 views • 13 slides

Restriction Enzymes. Presented by: Elizabeth Gordon April 11,2006. Function. (From Tock and Dryden 2005). Historical Perspective. (From Lewin 2003). Four Types. (From Tock and Dryden 2005). Type I. Three subunits form R 2 M 2 S 1
593 views • 15 slides

General Genetics. Lab # 7 Restriction Enzymes. Objectives:. Introduce the students to digest genomic DNA by restriction endonucleases . Observe the results of digestion on agarose gel electrophoresis. Theoretical Basis Using Restriction Enzymes.
552 views • 24 slides

Restriction Endonucleases Or Restriction Enzymes. What Are Restriction Enzymes. They are enzymes that act as molecular scissors because they are able to cut DNA at specific base pairs. Each restriction enzyme recognizes a characteristic sequence of nucleotides, this is the recognition site.
1.95k views • 17 slides
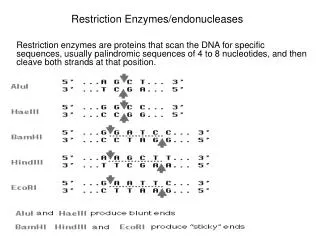
Restriction Enzymes/endonucleases. Restriction enzymes are proteins that scan the DNA for specific sequences, usually palindromic sequences of 4 to 8 nucleotides, and then cleave both strands at that position. Restriction enzymes are molecular scissors – they cut DNA
312 views • 7 slides

Restriction Enzymes. P roteins that cut DNA at specific sites. Recombinant DNA Technology. Is the ability to cleave and ligate (cut and paste), a functional piece of DNA predictably and precisely to enable biotechnologists to recombine DNA molecules.
347 views • 13 slides

ENZYMES THAT MODIFY DNA AND RNA 1. RESTRICTION ENDONUCLEASES AND METHYLASES RESTRICTION ENDONUCLEASES EXIST IN NATURE IN PROKARYOTES
453 views • 22 slides

Restriction Endonucleases. David Peterson. Structure of DNA and RNA. Information Flow in Cells. DNA RNA Protein. Transcription. Translation. Amino acids combine to make peptides and proteins. Enzymes. Catalyze reactions Most are proteins.
282 views • 15 slides

Restriction Enzymes and DNA Fingerprinting. Molecular Scissors for Cutting DNA Precisely. Its because of these biological catalysts that genetic engineering is possible Restriction enzymes can also be called Endonucleases. Types of Restriction Enzymes. Type I
382 views • 11 slides

Restriction Enzymes. What are restriction enzymes?. Restriction enzymes are proteins that cut DNA. Because they cut within the molecule, they are often referred to as restriction endo nucleases. Function. Found naturally in bacteria Protects the bacteria from invading viruses
477 views • 24 slides
Restriction Enzymes. Discovery. In 1962, Werner Arber, a Swiss biochemist, provided the first evidence for the existence of "molecular scissors" that could cut DNA.
274 views • 12 slides
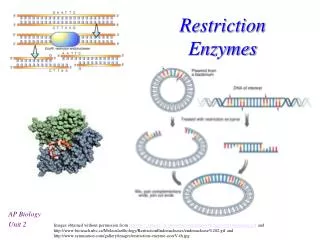
Restriction Enzymes. AP Biology Unit 2.
832 views • 10 slides
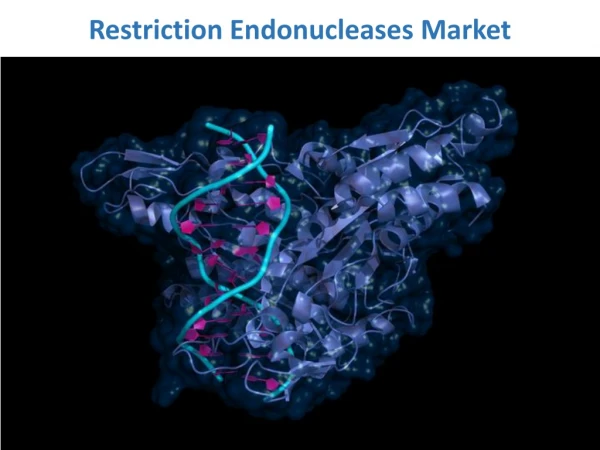
The factors that drive the growth of the restriction endonucleases market are increase in use of restriction endonucleases in various applications such as in vivo gene editing, epigenetic modifications, building DNA libraries, and others.

Restriction Enzymes. Molecular Scissors. Restriction enzymes are molecular scissors. Restriction Enzymes scan the DNA code Find a very specific set of nucleotides Make a specific cut. Picking a palindrome Words that read the same forwards as backwards. Hannah Level Madam. hannaH leveL
214 views • 15 slides